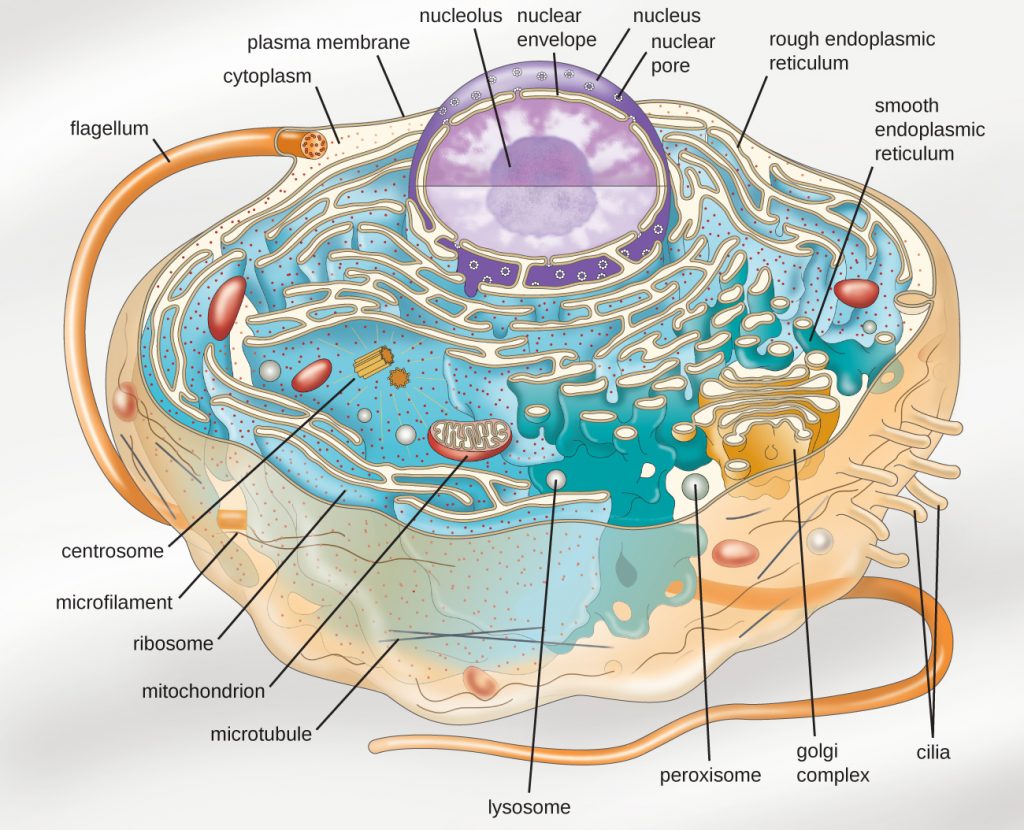
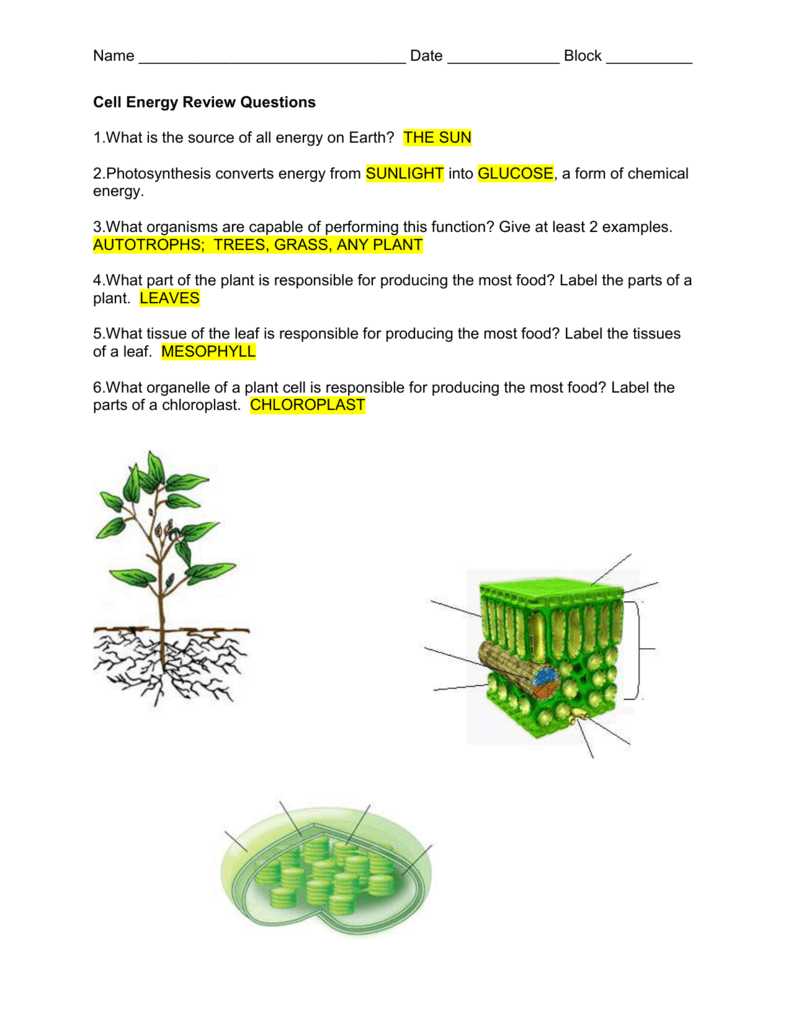
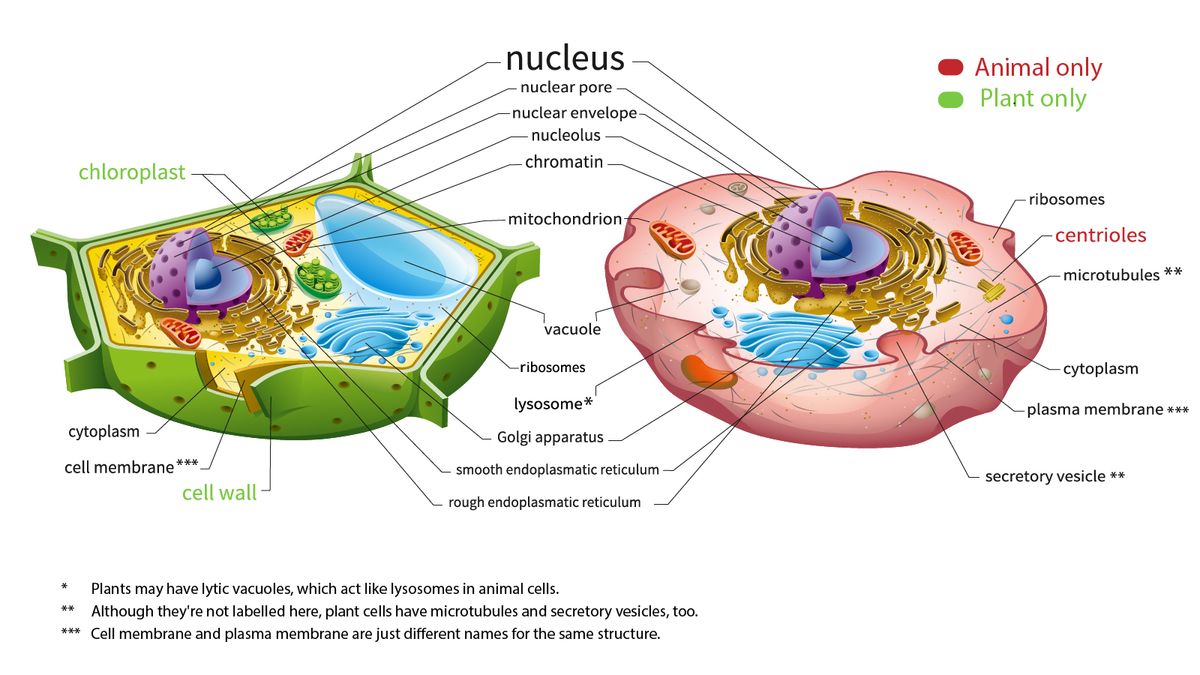
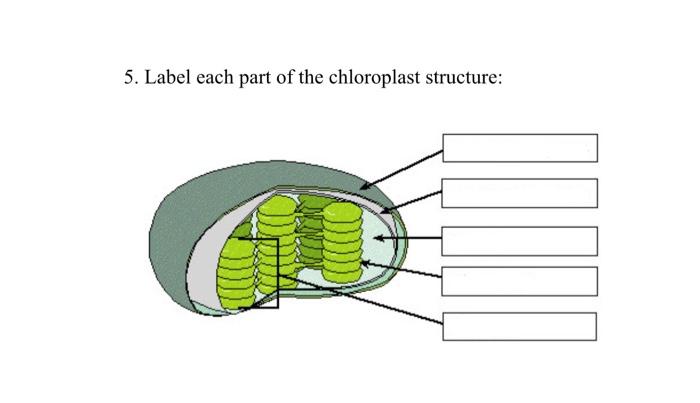
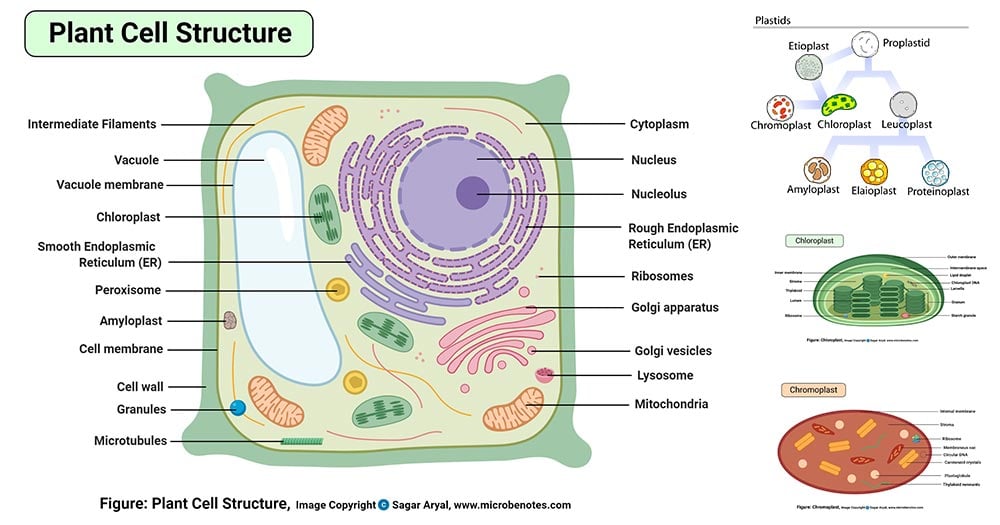
40 label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
Chloroplast - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary The chloroplast is one of the organelles of a photosynthetic eukaryotic cell. It is a type of plastid (the other types are chromoplasts and leucoplasts). The chloroplasts are identifiable from the other plastids by their color, shape, structure, and function. The chloroplasts are green due to the chlorophyll pigments that occur in abundance. Chloroplasts - Structure And Functions - A Level Biology The chloroplasts with the nucleus and cell membrane and ER are the key organelles of pathogen defense. The most important function of chloroplast is to make food by the process of photosynthesis. Food is prepared in the form of sugars. During the process of photosynthesis sugar and oxygen are made using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
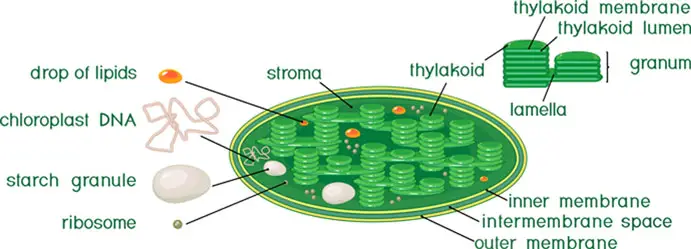
Chloroplast: Definition, Structure & Function (with Diagram) The stroma fluid contains the chloroplast DNA as well as proteins and starches. It is where the formation of carbohydrates from photosynthesis takes place. The Function of Chloroplast Ribosomes and Thylkaoids The ribosomes are clusters of proteins and nucleotides that manufacture enzymes and other complex molecules required by the chloroplast.

Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function
quizlet.com › 18614177 › parts-of-a-chloroplastparts of a chloroplast Flashcards | Quizlet forms a boundary between mitochondrion and cytoplasm; helps define the inner membrane space, smooth membrane in mitochondria intermembrane space the fluid filled space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, the region between the inner membrane and the outer membrane of a mitochondrion or a chloroplast. Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis - ThoughtCo Photosynthesis occurs in eukaryotic cell structures called chloroplasts. A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The main components of a chloroplast are protein (50 to 60%), lipids, pigments like carotenoids and chlorophyll, a small amount of RNA and DNA, traces of Vitamin E and K and minerals iron, magnesium, manganese, etc. A chloroplast is covered by a membranous envelope, inside which matrix and thylakoids are present.
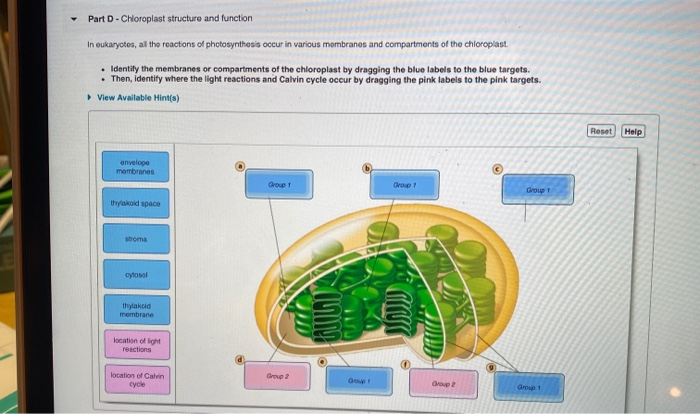
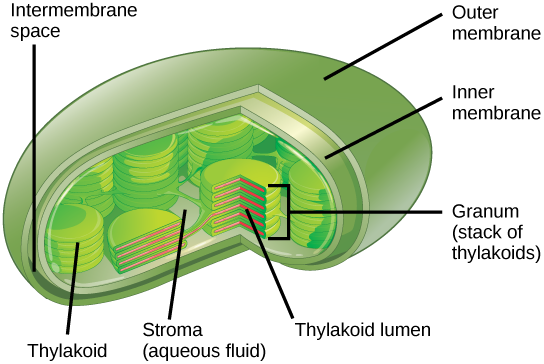
Label the parts of a chloroplast and identify its function. A Look Inside the Chloroplast: Organelle Components and Photosynthesis ... Parts of the chloroplast. The chloroplast has three membrane systems: the outer membrane, the inner membrane, and the thylakoid system. Thylakoids are disc-shaped and collect photons from a light source (usually the sun). They consist of a thylakoid membrane that surrounds the lumen. The lumen is where processes like oxygen evolution ... Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS The chloroplast structure consists of the following parts: Membrane Envelope It comprises inner and outer lipid bilayer membranes. The inner membrane separates the stroma from the intermembrane space. Intermembrane Space The space between inner and outer membranes. Thylakoid System (Lamellae) The system is suspended in the stroma. Photosynthesis, Chloroplast | Learn Science at Scitable - Nature The chloroplast is involved in both stages of photosynthesis. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid. There, water (H 2 O) is oxidized, and oxygen (O 2) is released. The electrons that ... Chloroplast structure and function Flashcards | Quizlet Chloroplast function Absorbs sunlight and converts it into sugar molecules and also produce free energy stored in the form of ATP and NADPH through photosynthesis Chloroplast size Varies from species to species System of 3 membranes Outer membrane, inner membrane and thylakoid Stroma contains...? Starch grains, and ribosomes Photosystems
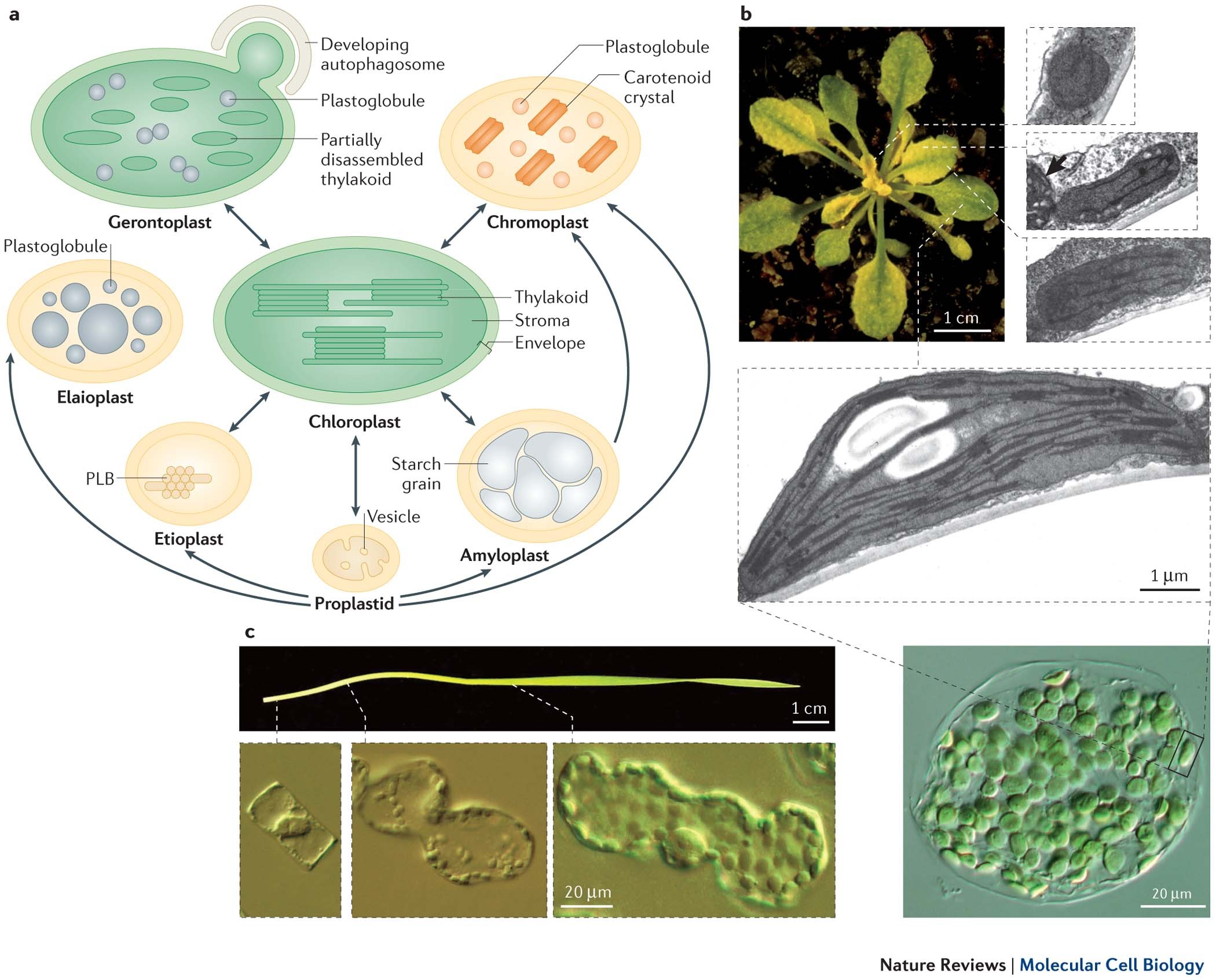
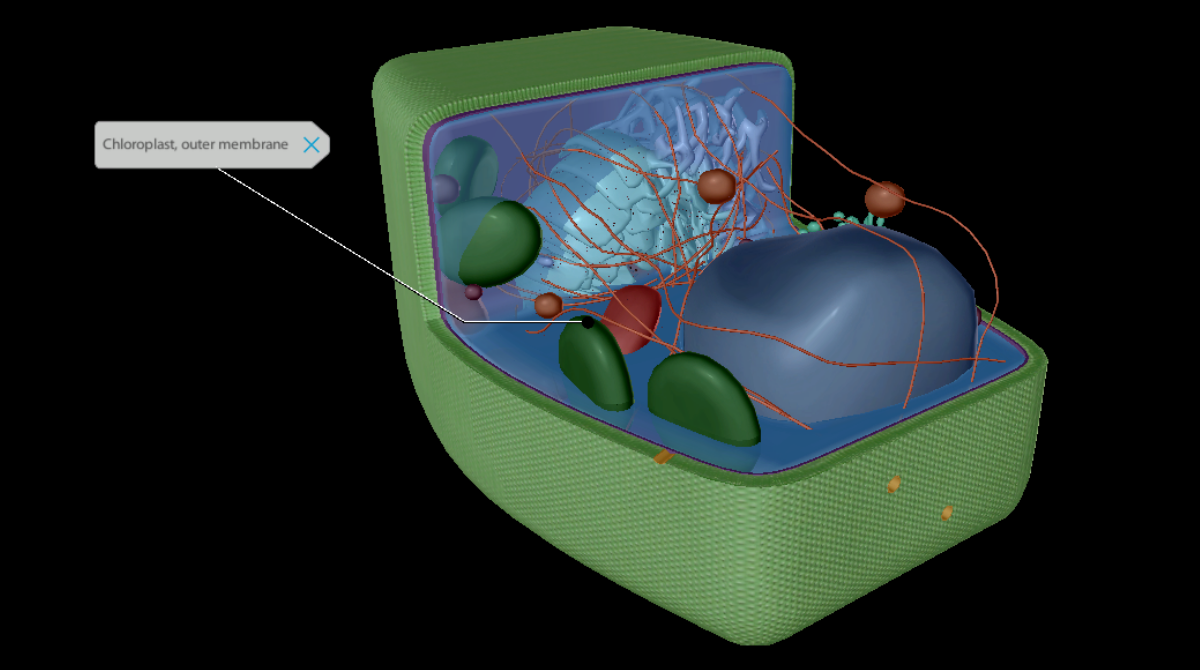
The students will label the parts of the chloroplast and give the function In addition of regulation activity, the fatty acids, lipids and carotenoids are synthesized in the inner chloroplast membrane. 3. Stroma . It contain the enzymes necessary for carbon fixation, it also manages the chloroplast response to cellular stresses and signaling between various organelles. 4. Thylakoid Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbe Notes Chloroplasts are a type of membrane-bound plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. It is this pigment that imparts a green color to plant parts and serves to capture light energy. Chloroplasts can be found in the cells of the mesophyll in plant leaves. Chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram Chloroplasts are a type of plastid—a round, oval, or disk-shaped body that is involved in the synthesis and storage of foodstuffs. Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green colour, which results from the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Chloroplasts - Definition, Structure, Function and Microscopy The circular DNA of chloroplast is refered to as cpDNA and helps regulate how the organelle functions. Membrane Compared to other organelles, chloroplasts have three types of membranes that serve different functions. These include: Smooth outer membrane (outer envelope membrane) Smooth inner membrane (inner envelope membrane)
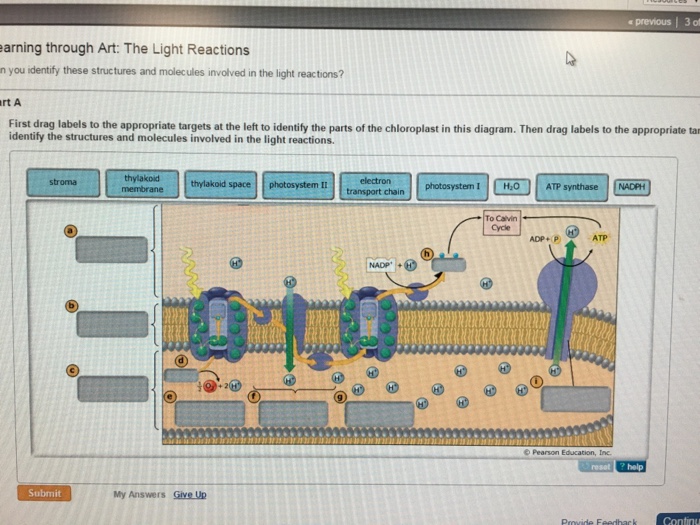
Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise Chloroplasts are plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix, and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. It is this pigment that imparts a green color to plant parts, and serves to capture light energy. A detailed account of the structure and functions of chloroplasts has been provided below. For each of the following processes, identify the part of the ... For each of the following processes, identify the part of the chloroplast in which it takes place. Light-dependent reactions: A-stroma , B-thylakoids Light-independent reactions: A- stroma , B-thylakoids ... An arrow from a location close to the ground marked D points towards Dead Organisms, which is a label under the animal. An arrow marked E ... Chloroplast: Diagram, Structure, Functions & More - Embibe One of the most important functions of the Chloroplast is to absorb light energy for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts consist of Stroma, inner membrane, outer membrane, thylakoid membrane, and intermembrane space. Chloroplast Analogy An analogy for chloroplasts is that chloroplasts are like a kitchen of the cell. Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary Function of Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the part of plant and algal cells that carry out photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy to energy stored in the form of sugar and other organic molecules that the plant or alga uses as food. Photosynthesis has two stages. In the first stage, the light-dependent reactions occur.
Labeling Chloroplast Diagram | Quizlet inner most cell membrane of chloroplast intermembrane space space between inner and outer membrane outer membrane membrane of chloroplast that is in contact with the cytosol of plant cell stroma liquid portion of chloroplast where Calvin Cycle (dark reactions) take place lumen of thylakoid space inside the thylakoid where light reactions occur.
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The main components of a chloroplast are protein (50 to 60%), lipids, pigments like carotenoids and chlorophyll, a small amount of RNA and DNA, traces of Vitamin E and K and minerals iron, magnesium, manganese, etc. A chloroplast is covered by a membranous envelope, inside which matrix and thylakoids are present.
Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis - ThoughtCo Photosynthesis occurs in eukaryotic cell structures called chloroplasts. A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
quizlet.com › 18614177 › parts-of-a-chloroplastparts of a chloroplast Flashcards | Quizlet forms a boundary between mitochondrion and cytoplasm; helps define the inner membrane space, smooth membrane in mitochondria intermembrane space the fluid filled space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, the region between the inner membrane and the outer membrane of a mitochondrion or a chloroplast.






















Komentar
Posting Komentar